DIY Cloud Weather Station with ESP32/ESP8266 (MySQL Database and PHP)
Build a cloud weather station dashboard to visualize your ESP32 or ESP8266 sensor readings from anywhere in the world. You’ll visualize your sensor data displayed on gauges and on a table. The ESP32 or ESP8266 will make an HTTP POST request to a PHP script to insert your data into a MySQL database.

Updated on 27 March 2023
Previously, we’ve stored sensor readings in a database and displayed them on a table or charts that you can access from anywhere using your own server. Now, I’ve decided to take a few steps further and add some more information to the web page.
I’ve added two gauges to display the latest temperature and humidity readings as well as some statistics about the minimum, maximum and average readings from a number of readings that you can define. You can also visualize all the latest readings on a table and you can select how many readings you want to show.
To build this project, you’ll use these technologies:
- ESP32 or ESP8266 programmed with Arduino IDE
- Hosting server and domain name
- PHP script to insert data into MySQL and display it on a web page
- MySQL database to store readings
Table of Contents
This project is divided into the following main sections:
- Hosting Your PHP Application and MySQL Database
- Preparing Your MySQL Database
- PHP Script HTTP POST – Receive and Insert Data in MySQL Database
- PHP Script for Database Functions
- PHP Script – Display Database Readings on Gauges and Table
- Setting Up the ESP32 or ESP8266
Watch the Video Demonstration
To see how the project works, you can watch the following video demonstration:
0. Download Source Code
For this project, you’ll need these files:
- SQL query to create your table: SensorData_Table.sql
- Insert and access database readings: esp-database.php
- Handle HTTP Post requests: esp-post-data.php
- CSS file to style your web page: esp-style.css
- Display your sensor readings: esp-weather-station.php
- Arduino Sketch for ESP32: HTTPS_ESP32_Cloud_Weather_Station.ino
- Arduino Sketch for ESP8266 : HTTPS_ESP8266_Cloud_Weather_Station.ino
- If your server doesn’t support HTTPS, use this Arduino Sketch (compatible with the ESP32 and ESP8266: ESP_HTTP_POST_MySQL.ino
- Download all projects files
1. Hosting Your PHP Application and MySQL Database
The goal of this project is to have your own domain name and hosting account that allows you to store sensor readings from the ESP32 or ESP8266. You can visualize the readings from anywhere in the world by accessing your own server domain.
Here’s a high-level overview of how the project works:
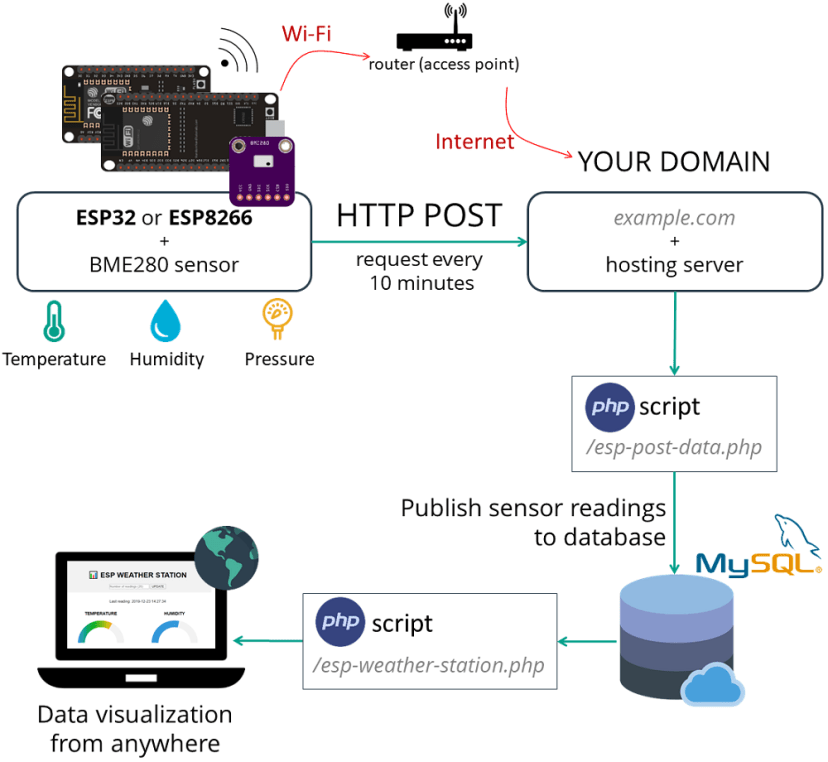
- You have an ESP32 or ESP8266 that sends sensor readings to your own server. For this, you have your board connected to your router;
- In your server, there’s a PHP script that allows you to store your readings in a MySQL database;
- Then, another PHP script will display the web page with the gauges, table, and all the other information;
- Finally, you can visualize the readings from anywhere in the world by accessing your own domain name.
Hosting Services
I recommend using one of the following hosting services that can handle all the project requirements:
- Bluehost (user-friendly with cPanel): free domain name when you sign up for the 3-year plan. I recommend choosing the unlimited websites option;
- Digital Ocean: Linux server that you manage through a command line. I only recommended this option for advanced users.
Those two services are the ones that I use and personally recommend, but you can use any other hosting service. Any hosting service that offers PHP and MySQL will work with this tutorial. If you don’t have a hosting account, I recommend signing up for Bluehost.
Get Hosting and Domain Name with Bluehost »
When buying a hosting account, you’ll also have to purchase a domain name. This is what makes this project interesting: you’ll be able to go to your domain name (https://example.com) and see your ESP readings.
If you like our projects, you might consider signing up for one of the recommended hosting services, because you’ll be supporting our work.
Note: you can also run a LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) server on a Raspberry Pi to access data in your local network. However, the purpose of this tutorial is to publish readings in your own domain name that you can access from anywhere in the world. This allows you to easily access your ESP readings without relying on a third-party IoT platform.
2. Preparing Your MySQL Database
After signing up for a hosting account and setting up a domain name, you can login to your cPanel or similar dashboard. After that, follow the next steps to create your database, username, password, and SQL table.
Creating a database and user
Open the “Advanced” tab:

1. Type “database” in the search bar and select “MySQL Database Wizard”.

2. Enter your desired Database name. In my case, the database name is esp_data. Then, press the “Next Step” button:

Note: later you’ll have to use the database name with the prefix that your host gives you (my database prefix in the screenshot above is blurred). I’ll refer to it as example_esp_data from now on.
3. Type your Database username and set a password. You must save all those details because you’ll need them later to establish a database connection with your PHP code.

That’s it! Your new database and user were created successfully. Now, save all your details because you’ll need them later:
- Database name: example_esp_data
- Username: example_esp_board
- Password: your password
Creating a SQL table
After creating your database and user, go back to cPanel dashboard and search for “phpMyAdmin”.

In the left sidebar, select your database name example_esp_data and open the “SQL” tab.

Important: make sure you’ve opened the example_esp_data database. Then, click the SQL tab. If you don’t follow these exact steps and run the SQL query, you might create a table in the wrong database.
Copy the SQL query in the following snippet:
CREATE TABLE SensorData (
id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
sensor VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
location VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
value1 VARCHAR(10),
value2 VARCHAR(10),
value3 VARCHAR(10),
reading_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
Paste it in the SQL query field (highlighted with a red rectangle) and press the “Go” button to create your table:

After that, you should see your newly created table called SensorData in the example_esp_data database as shown in the figure below:

3. PHP Script HTTP POST – Receive and Insert Data in MySQL Database
In this section, we’re going to create a PHP script that is responsible for receiving incoming requests from the ESP32 or ESP8266 and inserting the data into a MySQL database.
If you’re using a hosting provider with cPanel, you can search for “File Manager”:

Then, select the public_html option and press the “+ File” button to create a new .php file.

Note: if you’re following this tutorial and you’re not familiar with PHP or MySQL, I recommend creating these exact files. Otherwise, you’ll need to modify the ESP sketch provided with different URL paths.
Create a new file in /public_html with this exact name and extension: esp-post-data.php

Edit the newly created file (esp-post-data.php) and copy the following snippet:
<!--
Rui Santos
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/cloud-weather-station-esp32-esp8266/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-->
<?php
include_once('esp-database.php');
// Keep this API Key value to be compatible with the ESP code provided in the project page. If you change this value, the ESP sketch needs to match
$api_key_value = "tPmAT5Ab3j7F9";
$api_key= $sensor = $location = $value1 = $value2 = $value3 = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
$api_key = test_input($_POST["api_key"]);
if($api_key == $api_key_value) {
$sensor = test_input($_POST["sensor"]);
$location = test_input($_POST["location"]);
$value1 = test_input($_POST["value1"]);
$value2 = test_input($_POST["value2"]);
$value3 = test_input($_POST["value3"]);
$result = insertReading($sensor, $location, $value1, $value2, $value3);
echo $result;
}
else {
echo "Wrong API Key provided.";
}
}
else {
echo "No data posted with HTTP POST.";
}
function test_input($data) {
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
4. PHP Script for Database Functions
Create a new file in /public_html that is responsible for inserting and accessing data in your database. Name your file: esp-database.php

Copy that PHP script:
<!--
Rui Santos
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/cloud-weather-station-esp32-esp8266/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-->
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
// REPLACE with your Database name
$dbname = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_DATABASE_NAME";
// REPLACE with Database user
$username = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_USERNAME";
// REPLACE with Database user password
$password = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PASSWORD";
function insertReading($sensor, $location, $value1, $value2, $value3) {
global $servername, $username, $password, $dbname;
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO SensorData (sensor, location, value1, value2, value3)
VALUES ('" . $sensor . "', '" . $location . "', '" . $value1 . "', '" . $value2 . "', '" . $value3 . "')";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
return "New record created successfully";
}
else {
return "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
}
function getAllReadings($limit) {
global $servername, $username, $password, $dbname;
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, sensor, location, value1, value2, value3, reading_time FROM SensorData order by reading_time desc limit " . $limit;
if ($result = $conn->query($sql)) {
return $result;
}
else {
return false;
}
$conn->close();
}
function getLastReadings() {
global $servername, $username, $password, $dbname;
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, sensor, location, value1, value2, value3, reading_time FROM SensorData order by reading_time desc limit 1" ;
if ($result = $conn->query($sql)) {
return $result->fetch_assoc();
}
else {
return false;
}
$conn->close();
}
function minReading($limit, $value) {
global $servername, $username, $password, $dbname;
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT MIN(" . $value . ") AS min_amount FROM (SELECT " . $value . " FROM SensorData order by reading_time desc limit " . $limit . ") AS min";
if ($result = $conn->query($sql)) {
return $result->fetch_assoc();
}
else {
return false;
}
$conn->close();
}
function maxReading($limit, $value) {
global $servername, $username, $password, $dbname;
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT MAX(" . $value . ") AS max_amount FROM (SELECT " . $value . " FROM SensorData order by reading_time desc limit " . $limit . ") AS max";
if ($result = $conn->query($sql)) {
return $result->fetch_assoc();
}
else {
return false;
}
$conn->close();
}
function avgReading($limit, $value) {
global $servername, $username, $password, $dbname;
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT AVG(" . $value . ") AS avg_amount FROM (SELECT " . $value . " FROM SensorData order by reading_time desc limit " . $limit . ") AS avg";
if ($result = $conn->query($sql)) {
return $result->fetch_assoc();
}
else {
return false;
}
$conn->close();
}
?>
Before saving the file, you need to modify the $dbname, $username and $password variables with your unique details:
// Your Database name
$dbname = "example_esp_data";
// Your Database user
$username = "example_esp_board";
// Your Database user password
$password = "YOUR_USER_PASSWORD";After adding the database name, username and password, save the file and continue with this tutorial. If you try to access your domain name in the next URL path, you’ll see the following:
https://example.com/public_html/esp-post-data.php
5. PHP Script – Display Database Readings on Gauges and Table
You’ll also need to add a CSS file to style your dashboard, name it: esp-style.css:

Copy that CSS to your file and save it:
/**
Rui Santos
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/cloud-weather-station-esp32-esp8266/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
**/
body {
width: 60%;
margin: auto;
text-align: center;
font-family: Arial;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 800px) {
body {
width: 100%;
}
}
table {
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
}
div {
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
}
h2 { font-size: 2.5rem; }
.header {
padding: 1rem;
margin: 0 0 2rem 0;
background: #f2f2f2;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2rem;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.content {
display: flex;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 500px) /* Mobile */ {
.content {
flex-direction: column;
}
}
.mask {
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
display: block;
width: 12.5rem;
height: 6.25rem;
margin: 1.25rem;
}
.semi-circle {
position: relative;
display: block;
width: 12.5rem;
height: 6.25rem;
background: linear-gradient(to right, #3498db 0%, #05b027 33%, #f1c40f 70%, #c0392b 100%);
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50% / 100% 100% 0% 0%;
}
.semi-circle::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
left: 50%;
z-index: 2;
display: block;
width: 8.75rem;
height: 4.375rem;
margin-left: -4.375rem;
background: #fff;
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50% / 100% 100% 0% 0%;
}
.semi-circle--mask {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 12.5rem;
height: 12.5rem;
background: transparent;
transform: rotate(120deg) translate3d(0, 0, 0);
transform-origin: center center;
backface-visibility: hidden;
transition: all 0.3s ease-in-out;
}
.semi-circle--mask::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0%;
z-index: 2;
display: block;
width: 12.625rem;
height: 6.375rem;
margin: -1px 0 0 -1px;
background: #f2f2f2;
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50% / 100% 100% 0% 0%;
}
.gauge--2 .semi-circle { background: #3498db; }
.gauge--2 .semi-circle--mask { transform: rotate(20deg) translate3d(0, 0, 0); }
#tableReadings { border-collapse: collapse; }
#tableReadings td, #tableReadings th {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
padding: 10px;
}
#tableReadings tr:nth-child(even){ background-color: #f2f2f2; }
#tableReadings tr:hover { background-color: #ddd; }
#tableReadings th {
padding: 10px;
background-color: #2f4468;
color: white;
}
Finally, create another PHP file in the /public_html directory that will display all the database content on a web page. Name your new file: esp-weather-station.php

Edit the newly created file (esp-weather-station.php) and copy the following code:
<!--
Rui Santos
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/cloud-weather-station-esp32-esp8266/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-->
<?php
include_once('esp-database.php');
if (isset($_GET["readingsCount"])){
$data = $_GET["readingsCount"];
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
$readings_count = $_GET["readingsCount"];
}
// default readings count set to 20
else {
$readings_count = 20;
}
$last_reading = getLastReadings();
$last_reading_temp = $last_reading["value1"];
$last_reading_humi = $last_reading["value2"];
$last_reading_time = $last_reading["reading_time"];
// Uncomment to set timezone to - 1 hour (you can change 1 to any number)
//$last_reading_time = date("Y-m-d H:i:s", strtotime("$last_reading_time - 1 hours"));
// Uncomment to set timezone to + 7 hours (you can change 7 to any number)
//$last_reading_time = date("Y-m-d H:i:s", strtotime("$last_reading_time + 7 hours"));
$min_temp = minReading($readings_count, 'value1');
$max_temp = maxReading($readings_count, 'value1');
$avg_temp = avgReading($readings_count, 'value1');
$min_humi = minReading($readings_count, 'value2');
$max_humi = maxReading($readings_count, 'value2');
$avg_humi = avgReading($readings_count, 'value2');
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="esp-style.css">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<header class="header">
<h1>📊 ESP Weather Station</h1>
<form method="get">
<input type="number" name="readingsCount" min="1" placeholder="Number of readings (<?php echo $readings_count; ?>)">
<input type="submit" value="UPDATE">
</form>
</header>
<body>
<p>Last reading: <?php echo $last_reading_time; ?></p>
<section class="content">
<div class="box gauge--1">
<h3>TEMPERATURE</h3>
<div class="mask">
<div class="semi-circle"></div>
<div class="semi-circle--mask"></div>
</div>
<p style="font-size: 30px;" id="temp">--</p>
<table cellspacing="5" cellpadding="5">
<tr>
<th colspan="3">Temperature <?php echo $readings_count; ?> readings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Min</td>
<td>Max</td>
<td>Average</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><?php echo $min_temp['min_amount']; ?> °C</td>
<td><?php echo $max_temp['max_amount']; ?> °C</td>
<td><?php echo round($avg_temp['avg_amount'], 2); ?> °C</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
<div class="box gauge--2">
<h3>HUMIDITY</h3>
<div class="mask">
<div class="semi-circle"></div>
<div class="semi-circle--mask"></div>
</div>
<p style="font-size: 30px;" id="humi">--</p>
<table cellspacing="5" cellpadding="5">
<tr>
<th colspan="3">Humidity <?php echo $readings_count; ?> readings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Min</td>
<td>Max</td>
<td>Average</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><?php echo $min_humi['min_amount']; ?> %</td>
<td><?php echo $max_humi['max_amount']; ?> %</td>
<td><?php echo round($avg_humi['avg_amount'], 2); ?> %</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</section>
<?php
echo '<h2> View Latest ' . $readings_count . ' Readings</h2>
<table cellspacing="5" cellpadding="5" id="tableReadings">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Sensor</th>
<th>Location</th>
<th>Value 1</th>
<th>Value 2</th>
<th>Value 3</th>
<th>Timestamp</th>
</tr>';
$result = getAllReadings($readings_count);
if ($result) {
while ($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
$row_id = $row["id"];
$row_sensor = $row["sensor"];
$row_location = $row["location"];
$row_value1 = $row["value1"];
$row_value2 = $row["value2"];
$row_value3 = $row["value3"];
$row_reading_time = $row["reading_time"];
// Uncomment to set timezone to - 1 hour (you can change 1 to any number)
//$row_reading_time = date("Y-m-d H:i:s", strtotime("$row_reading_time - 1 hours"));
// Uncomment to set timezone to + 7 hours (you can change 7 to any number)
//$row_reading_time = date("Y-m-d H:i:s", strtotime("$row_reading_time + 7 hours"));
echo '<tr>
<td>' . $row_id . '</td>
<td>' . $row_sensor . '</td>
<td>' . $row_location . '</td>
<td>' . $row_value1 . '</td>
<td>' . $row_value2 . '</td>
<td>' . $row_value3 . '</td>
<td>' . $row_reading_time . '</td>
</tr>';
}
echo '</table>';
$result->free();
}
?>
<script>
var value1 = <?php echo $last_reading_temp; ?>;
var value2 = <?php echo $last_reading_humi; ?>;
setTemperature(value1);
setHumidity(value2);
function setTemperature(curVal){
//set range for Temperature in Celsius -5 Celsius to 38 Celsius
var minTemp = -5.0;
var maxTemp = 38.0;
//set range for Temperature in Fahrenheit 23 Fahrenheit to 100 Fahrenheit
//var minTemp = 23;
//var maxTemp = 100;
var newVal = scaleValue(curVal, [minTemp, maxTemp], [0, 180]);
$('.gauge--1 .semi-circle--mask').attr({
style: '-webkit-transform: rotate(' + newVal + 'deg);' +
'-moz-transform: rotate(' + newVal + 'deg);' +
'transform: rotate(' + newVal + 'deg);'
});
$("#temp").text(curVal + ' ºC');
}
function setHumidity(curVal){
//set range for Humidity percentage 0 % to 100 %
var minHumi = 0;
var maxHumi = 100;
var newVal = scaleValue(curVal, [minHumi, maxHumi], [0, 180]);
$('.gauge--2 .semi-circle--mask').attr({
style: '-webkit-transform: rotate(' + newVal + 'deg);' +
'-moz-transform: rotate(' + newVal + 'deg);' +
'transform: rotate(' + newVal + 'deg);'
});
$("#humi").text(curVal + ' %');
}
function scaleValue(value, from, to) {
var scale = (to[1] - to[0]) / (from[1] - from[0]);
var capped = Math.min(from[1], Math.max(from[0], value)) - from[0];
return ~~(capped * scale + to[0]);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
If you try to access your domain name in the following URL path, you’ll see the following:
https://example.com/esp-weather-station.php
That’s it! If you see that web page with empty values in your browser, it means that everything is ready. In the next section, you’ll learn how to insert data from your ESP32 or ESP8266 into the database.
6. Setting Up the ESP32 or ESP8266
This project is compatible with both the ESP32 and ESP8266 boards. You just need to assemble a simple circuit and upload the sketch provided to insert temperature, humidity, pressure, and more into your database every 10 minutes. The sketch is slightly different for each board.

Parts Required
For this example, we’ll get sensor readings from the BME280 sensor. Here’s a list of parts you need to build the circuit for this project:
- ESP32 board (read Best ESP32 dev boards)
- Alternative – ESP8266 board (read Best ESP8266 dev boards)
- BME280 sensor
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
You can use the preceding links or go directly to MakerAdvisor.com/tools to find all the parts for your projects at the best price!

Schematics
The BME280 sensor module we’re using communicates via I2C communication protocol, so you need to connect it to the ESP32 or ESP8266 I2C pins.
BME280 wiring to ESP32
The ESP32 I2C pins are:
- GPIO 22: SCL (SCK)
- GPIO 21: SDA (SDI)
So, assemble your circuit as shown in the next schematic diagram (Guide for ESP32 with BME280 and ESP32 BME280 Web Server).

Recommended reading: ESP32 Pinout Reference Guide
BME280 wiring to ESP8266
The ESP8266 I2C pins are:
- GPIO 5 (D1): SCL (SCK)
- GPIO 4 (D2): SDA (SDI)
Assemble your circuit as in the next schematic diagram if you’re using an ESP8266 board (read Guide for ESP8266 with BME280).

Recommended reading: ESP8266 Pinout Reference Guide
Installing Libraries
We’ll program the ESP32/ESP8266 using Arduino IDE, so you must have the ESP add-on installed in your Arduino IDE.
Follow one of the next tutorials depending on the board you’re using:
- Install the ESP32 Board in Arduino IDE – you also need to install the BME280 Library and Adafruit_Sensor library
- Install the ESP8266 Board in Arduino IDE – you also need to install the BME280 Library and Adafruit_Sensor library
ESP32 Code
Follow this section if you’re using an ESP32. For an ESP8266 click here.
After installing the necessary board add-ons, copy the following code to your Arduino IDE, but don’t upload it yet. You need to make some changes to make it work for you.
/*
Rui Santos
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/esp32-esp8266-mysql-database-php/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BME280.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_SSID";
const char* password = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PASSWORD";
// REPLACE with your Domain name and URL path or IP address with path
const char* serverName = "https://example.com/esp-post-data.php";
// Keep this API Key value to be compatible with the PHP code provided in the project page.
// If you change the apiKeyValue value, the PHP file /post-esp-data.php also needs to have the same key
String apiKeyValue = "tPmAT5Ab3j7F9";
String sensorName = "BME280";
String sensorLocation = "Office";
/*#include <SPI.h>
#define BME_SCK 18
#define BME_MISO 19
#define BME_MOSI 23
#define BME_CS 5*/
#define SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA (1013.25)
Adafruit_BME280 bme; // I2C
//Adafruit_BME280 bme(BME_CS); // hardware SPI
//Adafruit_BME280 bme(BME_CS, BME_MOSI, BME_MISO, BME_SCK); // software SPI
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.println("Connecting");
while(WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Connected to WiFi network with IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// (you can also pass in a Wire library object like &Wire2)
bool status = bme.begin(0x76);
if (!status) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BME280 sensor, check wiring or change I2C address!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
//Check WiFi connection status
if(WiFi.status()== WL_CONNECTED){
WiFiClientSecure *client = new WiFiClientSecure;
client->setInsecure(); //don't use SSL certificate
HTTPClient https;
// Your Domain name with URL path or IP address with path
https.begin(*client, serverName);
// Specify content-type header
https.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
// Prepare your HTTP POST request data
String httpRequestData = "api_key=" + apiKeyValue + "&sensor=" + sensorName
+ "&location=" + sensorLocation + "&value1=" + String(bme.readTemperature())
+ "&value2=" + String(bme.readHumidity()) + "&value3=" + String(bme.readPressure()/100.0F) + "";
Serial.print("httpRequestData: ");
Serial.println(httpRequestData);
// You can comment the httpRequestData variable above
// then, use the httpRequestData variable below (for testing purposes without the BME280 sensor)
//String httpRequestData = "api_key=tPmAT5Ab3j7F9&sensor=BME280&location=Office&value1=24.75&value2=49.54&value3=1005.14";
// Send HTTP POST request
int httpResponseCode = https.POST(httpRequestData);
// If you need an HTTP request with a content type: text/plain
//https.addHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain");
//int httpResponseCode = https.POST("Hello, World!");
// If you need an HTTP request with a content type: application/json, use the following:
//https.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
//int httpResponseCode = https.POST("{\"value1\":\"19\",\"value2\":\"67\",\"value3\":\"78\"}");
if (httpResponseCode>0) {
Serial.print("HTTP Response code: ");
Serial.println(httpResponseCode);
}
else {
Serial.print("Error code: ");
Serial.println(httpResponseCode);
}
// Free resources
https.end();
}
else {
Serial.println("WiFi Disconnected");
}
//Send an HTTP POST request every 30 seconds
delay(30000);
}
Setting your network credentials
You need to modify the following lines with your network credentials: SSID and password. The code is well commented on where you should make the changes.
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_SSID";
const char* password = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PASSWORD";Setting your serverName
You also need to type your domain name, so the ESP publishes the readings to your own server.
const char* serverName = "https://example.com/esp-post-data.php";Now, you can upload the code to your board.
Note: Most servers require you to make HTTPS requests. The code above makes HTTPS requests to be compliant with the requirements of most cloud servers nowadays.
Your server doesn’t support HTTPS? Use this code instead.
How the code works
This project is already quite long, so we won’t cover in detail how the code works, but here’s a quick summary:
- Import all the libraries to make it work;
- Set variables that you might want to change (apiKeyValue, sensorName, sensorLocation);
- The apiKeyValue is just a random string that you can modify. It’s used for security reasons, so only anyone that knows your API key can publish data to your database;
- Initialize the serial communication for debugging purposes;
- Establish a Wi-Fi connection with your router;
- Initialize the BME280 to get readings;
- Initialize a secure WiFi client.
Then, in the loop() is where you actually make the HTTP POST request every 10 minutes with the latest BME280 readings:
// Your Domain name with URL path or IP address with path
http.begin(serverName);
// Specify content-type header
http.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
// Prepare your HTTP POST request data
String httpRequestData = "api_key=" + apiKeyValue + "&sensor=" + sensorName + "&location=" + sensorLocation + "&value1=" + String(bme.readTemperature()) + "&value2=" + String(bme.readHumidity()) + "&value3=" + String(bme.readPressure()/100.0F) + "";
int httpResponseCode = http.POST(httpRequestData);You can comment the httpRequestData variable above that concatenates all the BME280 readings and use the httpRequestData variable below for testing purposes:
String httpRequestData = "api_key=tPmAT5Ab3j7F9&sensor=BME280&location=Office&value1=24.75&value2=49.54&value3=1005.14";Learn more about HTTPS Requests with the ESP32: ESP32 HTTPS Requests (Arduino IDE).
ESP8266 Code
Follow this section if you’re using an ESP8266. For an ESP32 check the section above.
After installing the necessary board add-ons and libraries, copy the following code to your Arduino IDE, but don’t upload it yet. You need to make some changes to make it work for you.
/*
Rui Santos
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/esp32-esp8266-mysql-database-php/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*/
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <ESP8266HTTPClient.h>
#include <WiFiClientSecureBearSSL.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BME280.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_SSID";
const char* password = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PASSWORD";
// REPLACE with your Domain name and URL path or IP address with path
const char* serverName = "https://example.com/esp-post-data.php";
// Keep this API Key value to be compatible with the PHP code provided in the project page.
// If you change the apiKeyValue value, the PHP file /post-esp-data.php also needs to have the same key
String apiKeyValue = "tPmAT5Ab3j7F9";
String sensorName = "BME280";
String sensorLocation = "Office";
/*#include <SPI.h>
#define BME_SCK 18
#define BME_MISO 19
#define BME_MOSI 23
#define BME_CS 5*/
#define SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA (1013.25)
Adafruit_BME280 bme; // I2C
//Adafruit_BME280 bme(BME_CS); // hardware SPI
//Adafruit_BME280 bme(BME_CS, BME_MOSI, BME_MISO, BME_SCK); // software SPI
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.println("Connecting");
while(WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Connected to WiFi network with IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// (you can also pass in a Wire library object like &Wire2)
bool status = bme.begin(0x76);
if (!status) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BME280 sensor, check wiring or change I2C address!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
//Check WiFi connection status
if(WiFi.status()== WL_CONNECTED){
std::unique_ptr<BearSSL::WiFiClientSecure>client(new BearSSL::WiFiClientSecure);
// Ignore SSL certificate validation
client->setInsecure();
//create an HTTPClient instance
HTTPClient https;
// Your Domain name with URL path or IP address with path
https.begin(*client, serverName);
// Specify content-type header
https.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
// Prepare your HTTP POST request data
String httpRequestData = "api_key=" + apiKeyValue + "&sensor=" + sensorName
+ "&location=" + sensorLocation + "&value1=" + String(bme.readTemperature())
+ "&value2=" + String(bme.readHumidity()) + "&value3=" + String(bme.readPressure()/100.0F) + "";
Serial.print("httpRequestData: ");
Serial.println(httpRequestData);
// You can comment the httpRequestData variable above
// then, use the httpRequestData variable below (for testing purposes without the BME280 sensor)
//String httpRequestData = "api_key=tPmAT5Ab3j7F9&sensor=BME280&location=Office&value1=24.75&value2=49.54&value3=1005.14";
// Send HTTP POST request
int httpResponseCode = https.POST(httpRequestData);
// If you need an HTTP request with a content type: text/plain
//http.addHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain");
//int httpResponseCode = https.POST("Hello, World!");
// If you need an HTTP request with a content type: application/json, use the following:
//http.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
//int httpResponseCode = https.POST("{\"value1\":\"19\",\"value2\":\"67\",\"value3\":\"78\"}");
if (httpResponseCode>0) {
Serial.print("HTTP Response code: ");
Serial.println(httpResponseCode);
}
else {
Serial.print("Error code: ");
Serial.println(httpResponseCode);
}
// Free resources
https.end();
}
else {
Serial.println("WiFi Disconnected");
}
//Send an HTTP POST request every 30 seconds
delay(30000);
}
Setting your network credentials
You need to modify the following lines with your network credentials: SSID and password. The code is well commented on where you should make the changes.
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_SSID";
const char* password = "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PASSWORD";Setting your serverName
You also need to type your domain name, so the ESP publishes the readings to your own server.
const char* serverName = "https://example.com/esp-post-data.php";Now, you can upload the code to your board.
Note: Most servers require you to make HTTPS requests. The code above makes HTTPS requests to be compliant with the requirements of most cloud servers nowadays.
Your server doesn’t support HTTPS? Use this code instead.
Learn more about HTTPS Requests with the ESP8266: ESP8266 NodeMCU HTTPS Requests (Arduino IDE).
Demonstration
After completing all the steps, let your ESP board collect some readings and publish them to your server.

If everything is correct, this is what you should see in your Arduino IDE Serial Monitor:

If you open your domain name in this URL path:
https://example.com/esp-weather-station.phpYou should see the latest 20 readings stored in your database. There are two gauges that show the latest temperature and humidity readings, and a timestamp.
Refresh the web page to see the latest readings:

There’s a field where you can type the number of readings to visualize, as well as the number of readings for these statistics: minimum, maximum, and average. By default, it’s set to 20. For example, if you type 30 and press the update button, you’ll see that your web page updates and recalculates all the values.

The web page is also mobile responsive, so you can use any device to access it:

You can also go to phpMyAdmin to manage the data stored in your SensorData table. You can delete it, edit, etc…

Wrapping Up
In this tutorial you’ve learned how to publish sensor data into a database in your own server domain that you can access from anywhere in the world. This requires that you have your own server and domain name (alternatively, you can use a Raspberry Pi LAMP Server for local access).
I encourage you to change the web page appearance, add more features (like email notifications), publish data from different sensors, use multiple ESP boards, and much more.
You might also like reading:
- ESP32/ESP8266 Send Email Notification using PHP Script
- Visualize Your Sensor Readings from Anywhere in the World (ESP32/ESP8266 + MySQL + PHP) using Charts
- ESP32 Relay Module Web Server
Learn more about the ESP32 and ESP8266 with our resources:
- Learn ESP32 with Arduino IDE
- Home Automation using ESP8266
- Build Web Servers with ESP32 and ESP8266
- Firebase Web App with ESP32 and ESP8266
- SMART HOME with Raspberry Pi, ESP32, and ESP8266
- Free ESP32 Projects and Tutorials…
- Free ESP8266 Projects and Tutorials…
Thank you for reading.













 Users Today : 4
Users Today : 4 Total Users : 33740
Total Users : 33740 Views Today : 6
Views Today : 6 Total views : 278833
Total views : 278833 Who's Online : 0
Who's Online : 0 Your IP Address : 216.73.216.238
Your IP Address : 216.73.216.238